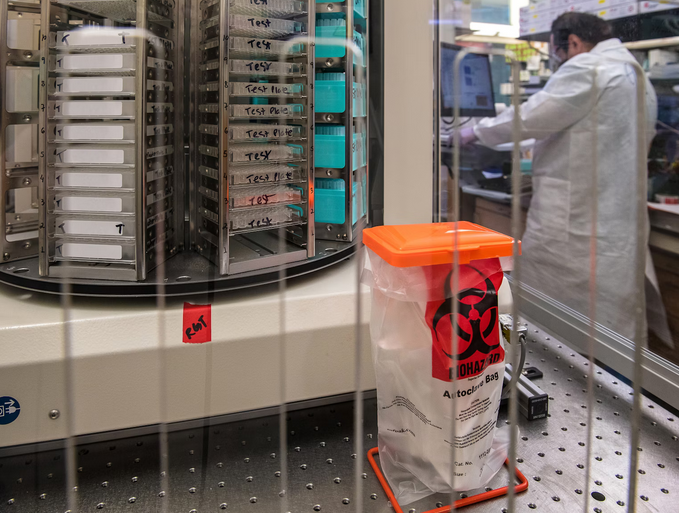
Biohazards are biological substances that pose a threat to human health or the environment. They can come from living organisms or their products, such as bacteria, viruses, toxins, and biological materials that can cause harm if exposed to humans. Understanding the types and risks associated with BioHazard Cleanup is crucial for safeguarding public health and implementing effective safety measures.
Types of Biohazards
Biological Agents
Biological agents include bacteria, viruses, fungi, parasites, and prions. These microorganisms can cause infections, diseases, and allergic reactions in humans. Examples include E. coli, influenza virus, anthrax bacteria, and malaria parasites.
Bloodborne Pathogens
Bloodborne pathogens are infectious microorganisms found in human blood and other bodily fluids. They can be transmitted through direct contact with infected blood or bodily fluids and can cause diseases such as HIV/AIDS, Hepatitis B, and Hepatitis C.
Toxins
Toxins are poisonous substances produced by living organisms, such as plants, animals, bacteria, and fungi. They can cause illness or death when absorbed, ingested, or inhaled. Examples include botulinum toxin produced by bacteria and aflatoxins produced by fungi.
Medical Waste
Medical waste includes materials generated in healthcare settings that may contain infectious agents or biohazardous substances. Improper disposal of medical waste can lead to the spread of infections and pose risks to waste handlers and the community.
Risks to Human Health
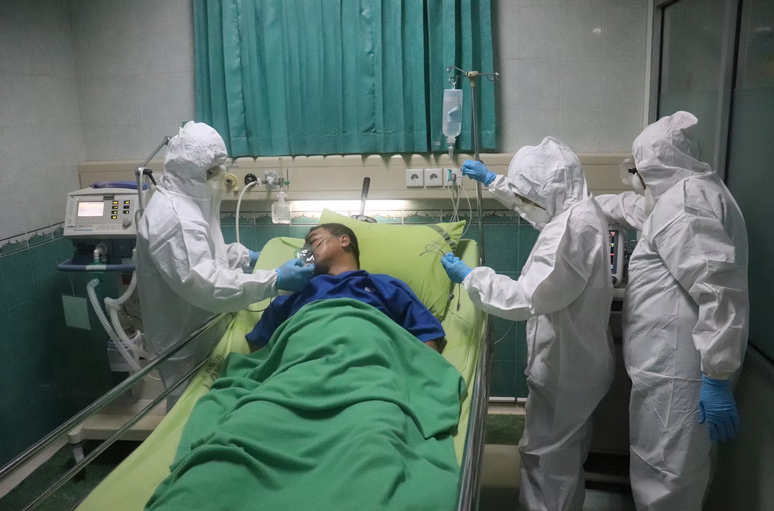
Biohazards pose several risks to human health, depending on the type of biohazard and the route of exposure:
- Infections and Diseases: Exposure to pathogenic microorganisms can lead to infections and diseases. For example, bacteria can cause skin infections, respiratory illnesses, or foodborne diseases.
- Allergic Reactions: Some biohazards, such as certain proteins or allergens from plants or animals, can trigger allergic reactions in susceptible individuals.
- Toxic Reactions: Exposure to toxins produced by microorganisms or plants can result in toxic reactions, affecting organs such as the liver, kidneys, or nervous system.
- Bloodborne Pathogen Transmission: Bloodborne pathogens can be transmitted through needlestick injuries, contaminated sharps, or contact with infected blood or bodily fluids, leading to serious infections.
Preventive Measures for Biohazards
Engineering Controls
Implementing engineering controls such as ventilation systems, biosafety cabinets, and sharps disposal containers to minimize exposure to biohazards in workplaces or healthcare settings.
Administrative Controls
Developing and implementing policies, procedures, and training programs to educate workers and the public about biohazard risks and safe handling practices.
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Use appropriate PPE such as gloves, masks, gowns, and eye protection to protect against exposure to biohazards and reduce the risk of infection or injury.
Understanding the types and risks associated with biohazards is essential for protecting human health and preventing the spread of infections and diseases. By implementing effective safety measures, educating individuals, and adhering to regulatory standards, communities and workplaces can mitigate the risks posed by biohazards and promote a safer environment for all. Stay informed, stay safe.
…



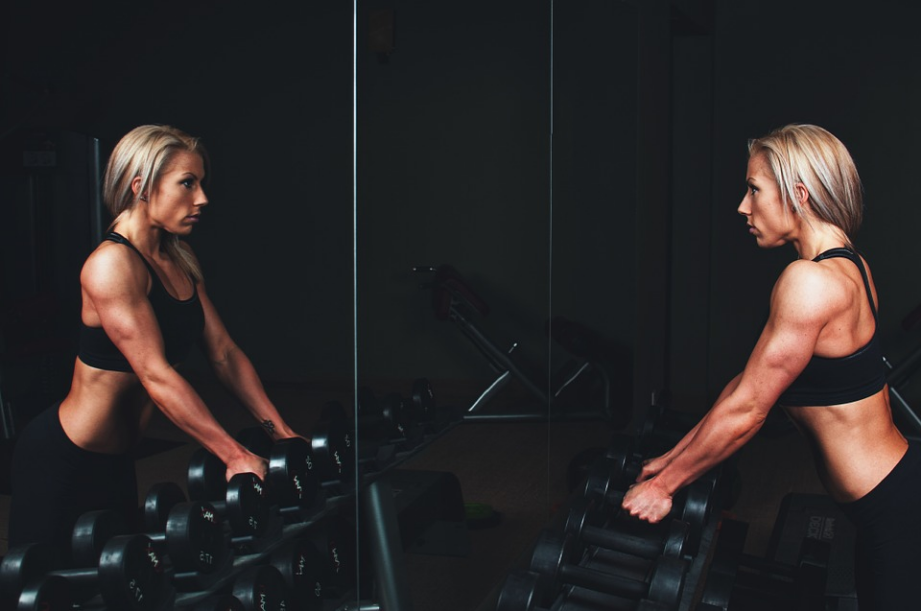
 The relentless pursuit of an idealized physique can sometimes take a toll on mental health. Bodybuilding often involves strict dietary regimens and intense training schedules, which may contribute to disordered eating patterns, body dysmorphia, and other psychological challenges. It is essential to acknowledge the holistic nature of health and wellness, encompassing both physical and mental aspects. While bodybuilding products can be effective tools for enhancing performance and achieving fitness goals, their usage should not come at the expense of overall health.
The relentless pursuit of an idealized physique can sometimes take a toll on mental health. Bodybuilding often involves strict dietary regimens and intense training schedules, which may contribute to disordered eating patterns, body dysmorphia, and other psychological challenges. It is essential to acknowledge the holistic nature of health and wellness, encompassing both physical and mental aspects. While bodybuilding products can be effective tools for enhancing performance and achieving fitness goals, their usage should not come at the expense of overall health.



 When it comes to boosting brain function, golf is a hole-in-one. The strategic nature of the game requires constant mental focus and concentration. As you navigate through each hole, your brain calculates distances, evaluates wind conditions, and determines the best approach for each shot. But golf isn’t just about the physical act of swinging a club – it also provides ample opportunities for problem-solving and decision-making. Every course presents unique challenges, from strategically placed bunkers to water hazards that demand careful navigation.
When it comes to boosting brain function, golf is a hole-in-one. The strategic nature of the game requires constant mental focus and concentration. As you navigate through each hole, your brain calculates distances, evaluates wind conditions, and determines the best approach for each shot. But golf isn’t just about the physical act of swinging a club – it also provides ample opportunities for problem-solving and decision-making. Every course presents unique challenges, from strategically placed bunkers to water hazards that demand careful navigation.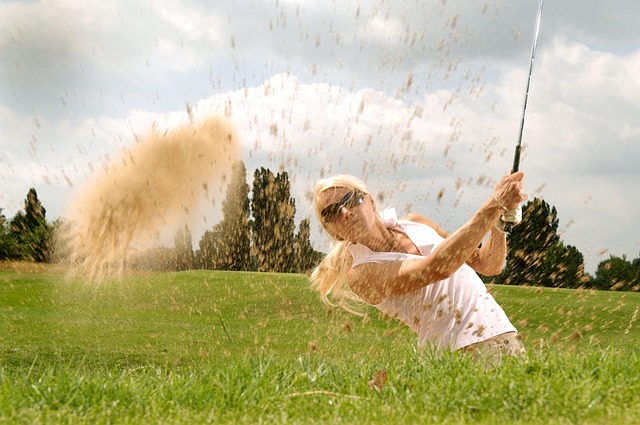
 Playing golf not only benefits physical health but also positively impacts mental well-being. The serene and picturesque environment of the golf course can help reduce stress and enhance relaxation. As you stroll through the green fairways, your mind is freed from the daily hustle and bustle, allowing you to focus on the game and enjoy some personal time. Golf is often considered a social sport, allowing players to connect with others. Whether playing with friends or joining a club, interacting with fellow golfers can boost your mood and create a sense of camaraderie.
Playing golf not only benefits physical health but also positively impacts mental well-being. The serene and picturesque environment of the golf course can help reduce stress and enhance relaxation. As you stroll through the green fairways, your mind is freed from the daily hustle and bustle, allowing you to focus on the game and enjoy some personal time. Golf is often considered a social sport, allowing players to connect with others. Whether playing with friends or joining a club, interacting with fellow golfers can boost your mood and create a sense of camaraderie.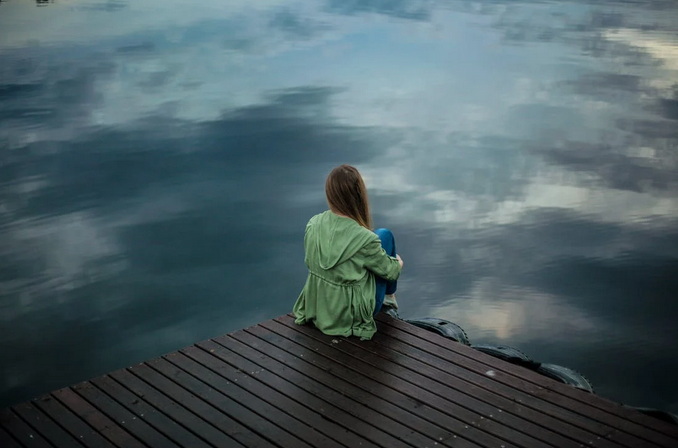
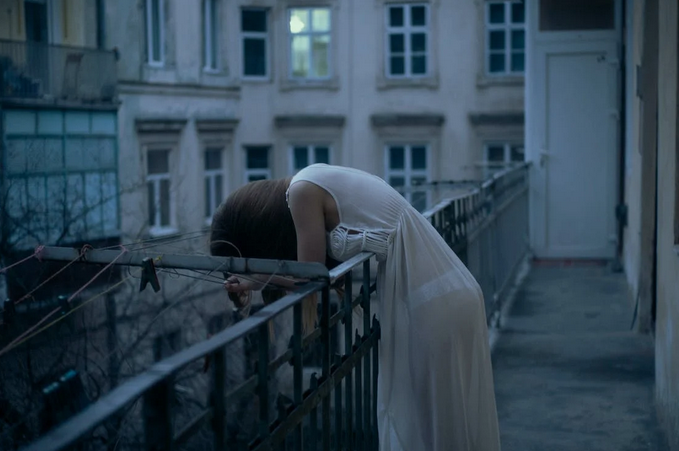

 Depression is a serious mental health disorder that should never be taken lightly. Untreated depression can lead to thoughts of suicide or a lack of willingness to live. People with depression are at an increased risk for suicide and should be monitored closely if they are exhibiting any signs of suicidal thinking or behavior.
Depression is a serious mental health disorder that should never be taken lightly. Untreated depression can lead to thoughts of suicide or a lack of willingness to live. People with depression are at an increased risk for suicide and should be monitored closely if they are exhibiting any signs of suicidal thinking or behavior.
 Buying expensive supplements from the store is probably best because professionals will have tested them to make sure that there are no dangerous ingredients in them! There are many different types of herbal supplements available for purchase, and it’s important to know what you’re looking for before spending money on any supplement. When buying supplements, one common mistake is purchasing cheap, unproven products from online stores. These supplements may not be safe to take and could cause more harm than good. It’s essential to do your research before buying any supplement and only purchase proven effective and safe.
Buying expensive supplements from the store is probably best because professionals will have tested them to make sure that there are no dangerous ingredients in them! There are many different types of herbal supplements available for purchase, and it’s important to know what you’re looking for before spending money on any supplement. When buying supplements, one common mistake is purchasing cheap, unproven products from online stores. These supplements may not be safe to take and could cause more harm than good. It’s essential to do your research before buying any supplement and only purchase proven effective and safe. Finally, it’s essential to consider where you’re buying your supplements and how they are stored. If possible, but only those that have been organically grown without the use of pesticides or dangerous chemicals. You should also make sure to keep them in a cool place away from direct sunlight, as heat can break down their active ingredients over time. By following these simple tips, you can avoid making costly mistakes when buying herbal supplements!
Finally, it’s essential to consider where you’re buying your supplements and how they are stored. If possible, but only those that have been organically grown without the use of pesticides or dangerous chemicals. You should also make sure to keep them in a cool place away from direct sunlight, as heat can break down their active ingredients over time. By following these simple tips, you can avoid making costly mistakes when buying herbal supplements!
 When planning on buying
When planning on buying  When purchasing weight loss supplements, another vital factor you need to consider is the ingredients. Before you head to the market, you need to understand that various active components help in the fat-burning process. Therefore, consider choosing the right supplements with natural ingredients.
When purchasing weight loss supplements, another vital factor you need to consider is the ingredients. Before you head to the market, you need to understand that various active components help in the fat-burning process. Therefore, consider choosing the right supplements with natural ingredients.



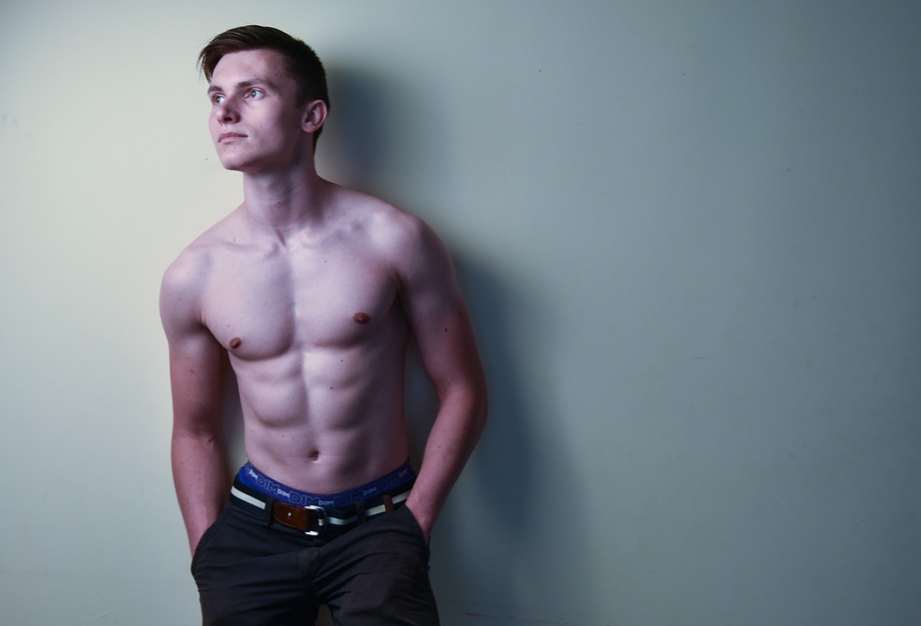
 In recent years, the popularity of female bodybuilding has increased considerably. The number of girls who are into bodybuilding is growing day by day. Now women can see that lifting weights and eating right will not turn them into big, bulky individuals. However, some women want to
In recent years, the popularity of female bodybuilding has increased considerably. The number of girls who are into bodybuilding is growing day by day. Now women can see that lifting weights and eating right will not turn them into big, bulky individuals. However, some women want to  Despite rumors that legal steroids don’t work, real women can expect good results from taking legal steroids. This is one of the best decisions if you want to achieve that gains. Legal steroids can help you build muscle, increase strength and give you more energy to train harder and longer without worrying about side effects.
Despite rumors that legal steroids don’t work, real women can expect good results from taking legal steroids. This is one of the best decisions if you want to achieve that gains. Legal steroids can help you build muscle, increase strength and give you more energy to train harder and longer without worrying about side effects.
 To build muscles, you should work out regularly in the gym. Lifting weight is the standard exercise for building muscles. A mistake that some people make when they are working out is not increasing the intensity. To get significant results, lift more weights.
To build muscles, you should work out regularly in the gym. Lifting weight is the standard exercise for building muscles. A mistake that some people make when they are working out is not increasing the intensity. To get significant results, lift more weights. The last thing you should consider to build more muscles is eating the right foods. Many people are out of shape as a result of the type of foods they eat. You should ensure that you eat a
The last thing you should consider to build more muscles is eating the right foods. Many people are out of shape as a result of the type of foods they eat. You should ensure that you eat a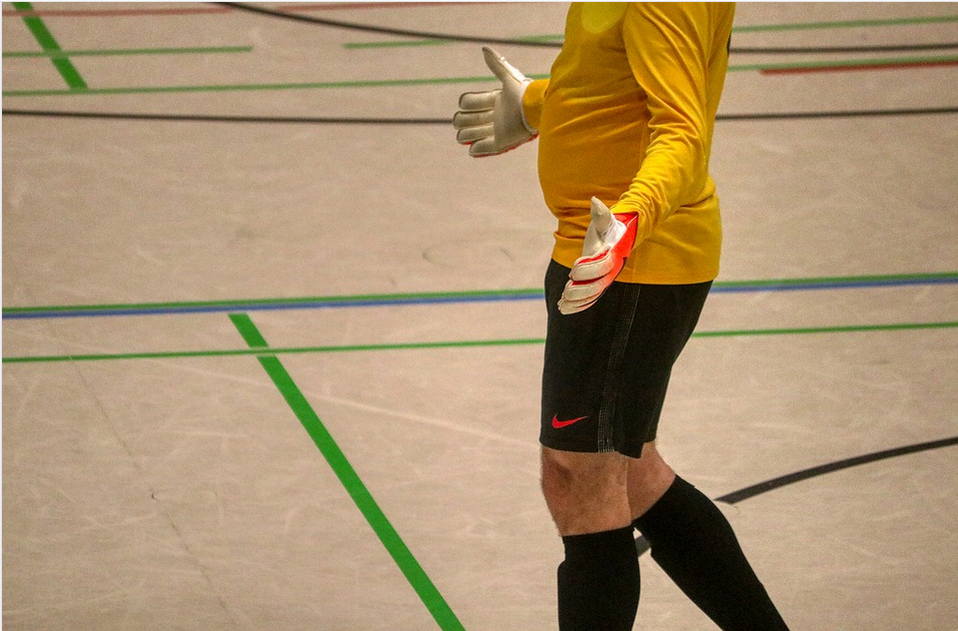 
 The game of soccer is entertaining, but for players, especially goalkeepers, without suitable gloves, they can easily suffer from injuries when they catch the ball every time. Goalkeepers can get cuts if they do not use professional goalkeeping gloves. This can affect the goalkeepers’ confidence as they will not have the guts to gather the ball because of the fear of getting injured.
The game of soccer is entertaining, but for players, especially goalkeepers, without suitable gloves, they can easily suffer from injuries when they catch the ball every time. Goalkeepers can get cuts if they do not use professional goalkeeping gloves. This can affect the goalkeepers’ confidence as they will not have the guts to gather the ball because of the fear of getting injured. Without suitable gloves, a soccer goalkeeper might not perform well in certain weather conditions. Sometimes, soccer is played in the cold winter, rainy days, or the hot summer, and the goalkeeper must wear gloves that fit well in both of these situations.
Without suitable gloves, a soccer goalkeeper might not perform well in certain weather conditions. Sometimes, soccer is played in the cold winter, rainy days, or the hot summer, and the goalkeeper must wear gloves that fit well in both of these situations.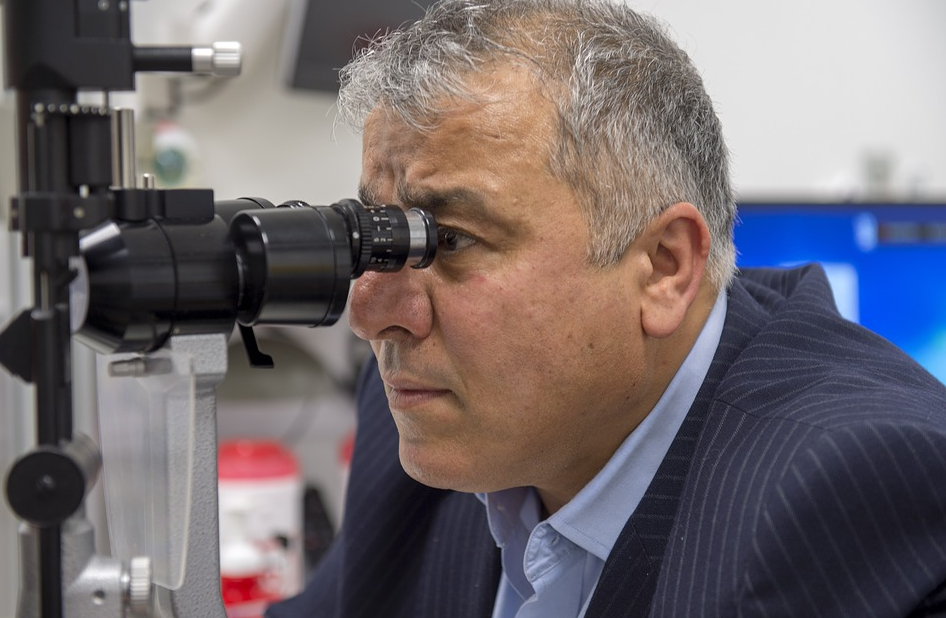
 The first thing you should consider when looking for an eye care center is the doctors’ qualification. Since your eyes are one of the most delicate and venerable parts of your body, you want to be sure that the one checking or treating them knows what they are doing.
The first thing you should consider when looking for an eye care center is the doctors’ qualification. Since your eyes are one of the most delicate and venerable parts of your body, you want to be sure that the one checking or treating them knows what they are doing. The next thing you should consider is the type of services an eye center offers. It will be crucial to note that the field of eye care is vast, and there are many types of areas a doctor or eye care center can specialize in. You should make sure that you research the type of eye care services offered in various eye care centers.
The next thing you should consider is the type of services an eye center offers. It will be crucial to note that the field of eye care is vast, and there are many types of areas a doctor or eye care center can specialize in. You should make sure that you research the type of eye care services offered in various eye care centers.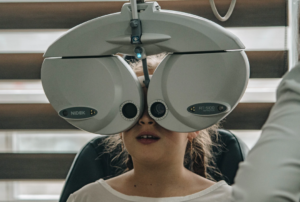 The next thing you should consider is the reputation an eye center has. If you are looking for a center in your area, you can ask others what they know about a given eye care center.
The next thing you should consider is the reputation an eye center has. If you are looking for a center in your area, you can ask others what they know about a given eye care center.
 When you decide you need the right SARM for cutting, one of the essential elements you need to do is conduct thorough research. As stated above, there are multiple supplements or drugs you are likely to find in most stores. However, you need to start by visiting your professional doctor to help you know some reliable sources you need to use to gather the right info. If your main aim is to cut, ensure that you identify the best SARMs stacks that work together well.
When you decide you need the right SARM for cutting, one of the essential elements you need to do is conduct thorough research. As stated above, there are multiple supplements or drugs you are likely to find in most stores. However, you need to start by visiting your professional doctor to help you know some reliable sources you need to use to gather the right info. If your main aim is to cut, ensure that you identify the best SARMs stacks that work together well. Ideally, it is advisable to understand that you will get various types of SARMs in the market. If you are a newbie, take your time and read through the label to check on the ingredients used. It is among the best thing you can do, especially when you want to pick the perfect supplement that will enable you to attain your cutting needs. Therefore, as a beginner, it is advisable to choose Ostarine and Cardarine.
Ideally, it is advisable to understand that you will get various types of SARMs in the market. If you are a newbie, take your time and read through the label to check on the ingredients used. It is among the best thing you can do, especially when you want to pick the perfect supplement that will enable you to attain your cutting needs. Therefore, as a beginner, it is advisable to choose Ostarine and Cardarine. When you plan to purchase the right SARMs, you need to take your time and identify the perfect place where you need to shop for these drugs. With advancements in the technology sector, most consumers consider online shopping because it offers buyers an opportunity to compare different products. If you want to purchase quality SARM at an affordable cost, take your time to research and find a reliable site where you can order your product and get it at your doorstep.
When you plan to purchase the right SARMs, you need to take your time and identify the perfect place where you need to shop for these drugs. With advancements in the technology sector, most consumers consider online shopping because it offers buyers an opportunity to compare different products. If you want to purchase quality SARM at an affordable cost, take your time to research and find a reliable site where you can order your product and get it at your doorstep.
 Everyone is different. For instance, the amount of food that you might be required to eat to gain one pound might be different from that consumed by another person with similar biological features. It is essential for starters that you understand your current calorie needs and the amount that you should increase to gain weight. As far as gaining weight is concerned, it is advisable to eat at least 500 more calories than what you burn.
Everyone is different. For instance, the amount of food that you might be required to eat to gain one pound might be different from that consumed by another person with similar biological features. It is essential for starters that you understand your current calorie needs and the amount that you should increase to gain weight. As far as gaining weight is concerned, it is advisable to eat at least 500 more calories than what you burn.